“Beam me up, Scotty!” For decades, this was cold science fiction until quantum physicists took it seriously and made it happen. Though no one has yet disappeared in a flash of light, the realm of quantum teleportation is now bound from the science fiction pages into the backbone of the internet of tomorrow.

Recent tests have broken expectations, showing that quantum information is now being teleported through actual fiber-optic cables, over distances once unthinkable. This listicle explores the science, milestones, and exciting future applications enabled by quantum teleportation for secure communication, distributed computing, and more. Here’s what every researcher, tech enthusiast, and quantum aficionado needs to know about the most significant breakthrough in information transfer since the invention of the Internet.
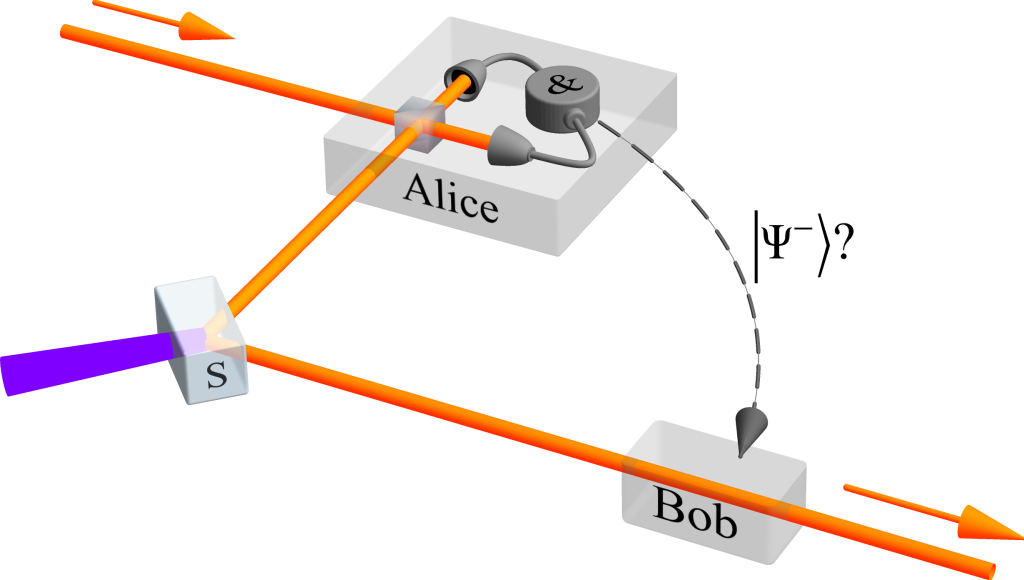
1. Quantum Teleportation: From Science Fiction to Fiber Optics
Teleportation has long been science fiction’s trusty standby, but quantum physics brings it a hard-nosed, if duller, reality. In quantum teleportation, not matter, but the quantum state, the exact set of characteristics that describe a particle, is moved. Through entanglement, two particles are linked so that the state of one instantly affects the other irrespective of distance. This feat, as outlined in new research, permits information to jump over space without going along the way between. Not a question of moving objects, but moving information itself a distinction that is rewriting the future of communication.

2. The 18-Mile Leap: Teleportation Over Public Networks
Recently, scientists teleported quantum information through 18 miles of regular fiber-optic cable, not in a sealed lab, but over a public network. The test, conducted by teams from Caltech, Fermilab, AT&T, Harvard, and NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, is a crucial step toward rolling out quantum technology over existing infrastructure. This is a major step towards developing a technology that will revolutionize how the world communicates,” remarks Panagiotis Spentzouris of Fermilab. The experiment achieved a fidelity of more than 90%, with the teleported quantum states being almost indistinguishable from the originals, even in real-world environments.

3. Entanglement: The Weird Teleportation Engine
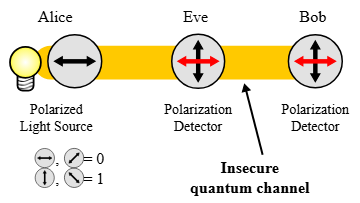
Quantum teleportation is based on the process of entanglement. When particles become entangled, their state is so intimately connected that to measure one directly determines the state of the other, regardless of how far away they are. Since quantum states cannot ever be copied, thanks to the no-cloning theorem, but only sent, entanglement is the ideal method of secure communication. This is not an abstraction; it forms the foundation of quantum key distribution schemes and the nascent quantum internet, which makes any attempt at intercepting a quantum message immediately detectable.
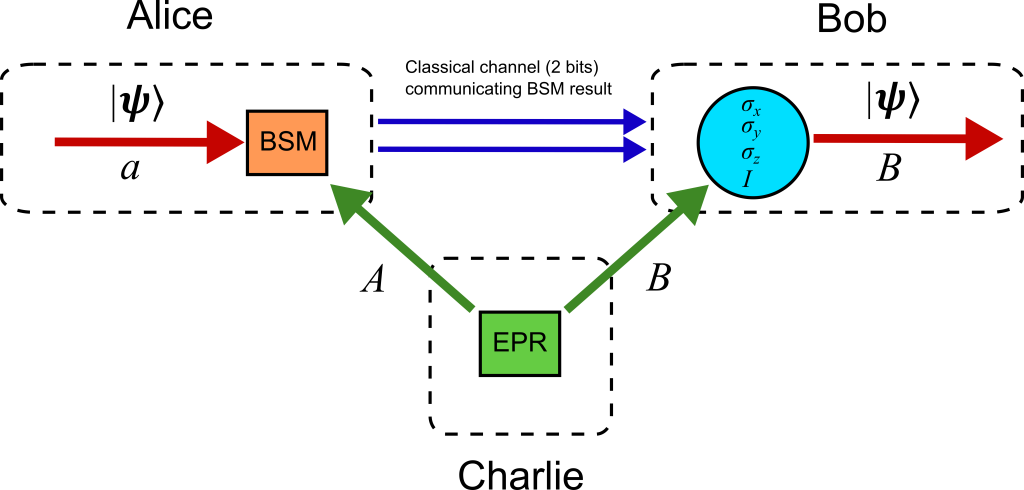
4. Quantum Repeaters: The Future Frontier in International Networks
Whereas classical repeaters boost signals for long-distance transmission, quantum repeaters must overcome the task of sending precarious quantum states without breaching the no-cloning principle. Recent experiments, including those of Victor Krutyanskiy’s group at the University of Innsbruck, have successfully shown quantum repeaters connecting nodes 50 kilometers apart. The devices employ entanglement swapping and quantum memory to increase the distance of quantum networks, a significant step toward scaling teleportation beyond city boundaries. As explained by Paul Kwiat of Q-NEXT, “That will require creating quantum repeaters.” They are now recognized as the key to developing a working, large-scale quantum internet.
5. Interoperability with Classical Networks: No New Cables Needed
One massive question has been whether it would be possible to overlay quantum communication on classical internet traffic. Northwestern University engineers have recently demonstrated that it can teleport quantum states over the current fiber-optic cables that transmit classical data. Our experiment demonstrates a route to next-generation quantum and classical networks that would all be derived from a common fiber-optic infrastructure,” said project lead Prem Kumar. With the right wavelength and eliminating the noise, the scientists were able to guarantee that delicate quantum signals reached their destination intact, even in the presence of millions of classical photons. It is good news because quantum improvements might be able to ride along on the existing internet infrastructure, accelerating deployment exponentially.
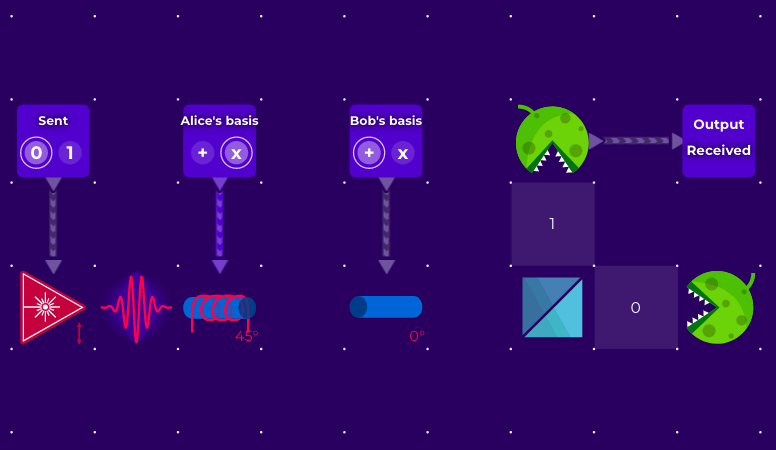
6. Ultra-Secure Communication and Quantum Key Distribution
Ultra-secure communication is best represented as the most promising use of quantum teleportation. Quantum key distribution (QKD) is based on the no-cloning theorem and entanglement to produce encryption keys that are inherently resistant to eavesdropping. According to recent research, any attempt to eavesdrop on to intercept a quantum key changes its state, instantly alerting the receiver and sender. This capability is guaranteed to transform cybersecurity, rendering data breaches and man-in-the-middle attacks unthinkable. Underlying the quantum internet is a universe in which privacy is not just a fantasy, but an assurance.
7. The Road Ahead: Scaling Up and Real-World Impact
Even with phenomenal progress, however, there are still obstacles to be overcome. Quantum internet to hundreds or thousands of miles will need breakthroughs in quantum repeaters, error correction, and fault-tolerant network protocols. But the current is irrevocable: test networks already are in the works in China and the United States, and researchers expect initial incarnations of a quantum internet during this decade. The repercussions stretch far beyond secure communication, allowing distributed quantum computing, ultraprecise sensing, and new types of scientific collaborations. As Maria Spiropulu of Caltech concisely stated, “We are incredibly proud to have achieved this milestone in sustainable, high-performance and scalable quantum teleportation systems.”
Quantum teleportation has gone from lab curiosity to working technology, ready to revolutionize the exchange, protection, and calculation of information. Teleporting human beings is still a pipedream, but the ability to transfer quantum states over networks in the real world is revealing to us a world where communication is not only faster and more secure, but of a different kind. The quantum internet is no longer a dream, it’s rapidly becoming a concrete reality, one entangled photon at a time.


