
As per history records, what things are needed regarding building the most powerful rocket ever made? For many years, engineers have actually worked hard to make rockets carry heavier things into space. They definitely keep improving engines, fuel, and rocket design to send bigger loads beyond Earth. We are seeing a family of huge rockets whose power numbers are only as amazing as their space missions. As per aerospace engineering standards, these rockets represent the best technology from Moon landings to Mars missions. Regarding space exploration, they show the highest level of engineering work.
Today’s competition for heavy-lift rockets is surely happening across the world, with the United States, China, and Russia all working on super-heavy designs. Moreover, these countries are either already using such rockets or are still developing them. Further, we are seeing some rockets that are already working legends, while others are only prototype models trying to change how we travel in space. This list ranks the top 10 rockets as per their raw thrust power and also covers their engineering achievements, operational records, and future roles regarding deep-space exploration.

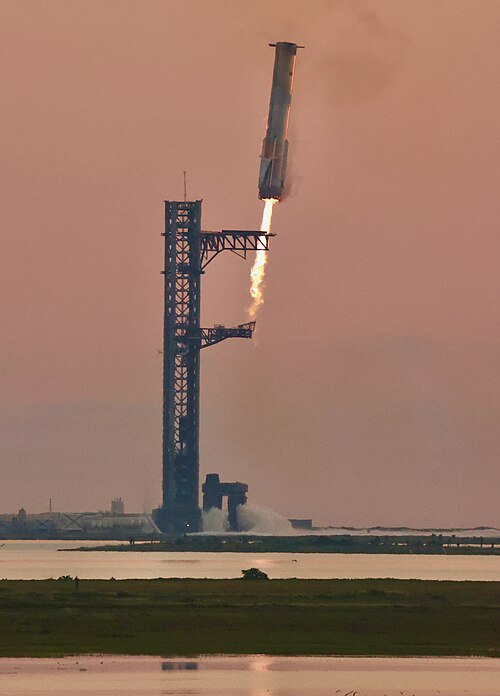
1. SpaceX Super Heavy Booster
The SpaceX Super Heavy booster actually holds the world record right now, definitely giving about 16.7 million pounds of push power when it starts. Moreover, this output is surely more than twice what the Saturn V rocket could produce. Moreover, it represents a significant increase in power capability. Basically when you put it with the Starship upper stage, the same system gives more than 29 million pounds of thrust, making it the most powerful rocket humanity has built.
Moreover, super Heavy actually uses 33 Raptor 2 engines that burn methane and liquid oxygen, and each engine definitely produces 2,255 kN of thrust in a full-flow staged combustion cycle. The design actually focuses on using the same vehicle many times, and it will definitely carry cargo to the moon and transport crew to Mars. We are seeing SpaceX test their rocket systems many times during actual flights, and this approach is only helping them prepare Starship for big missions in the next ten years.

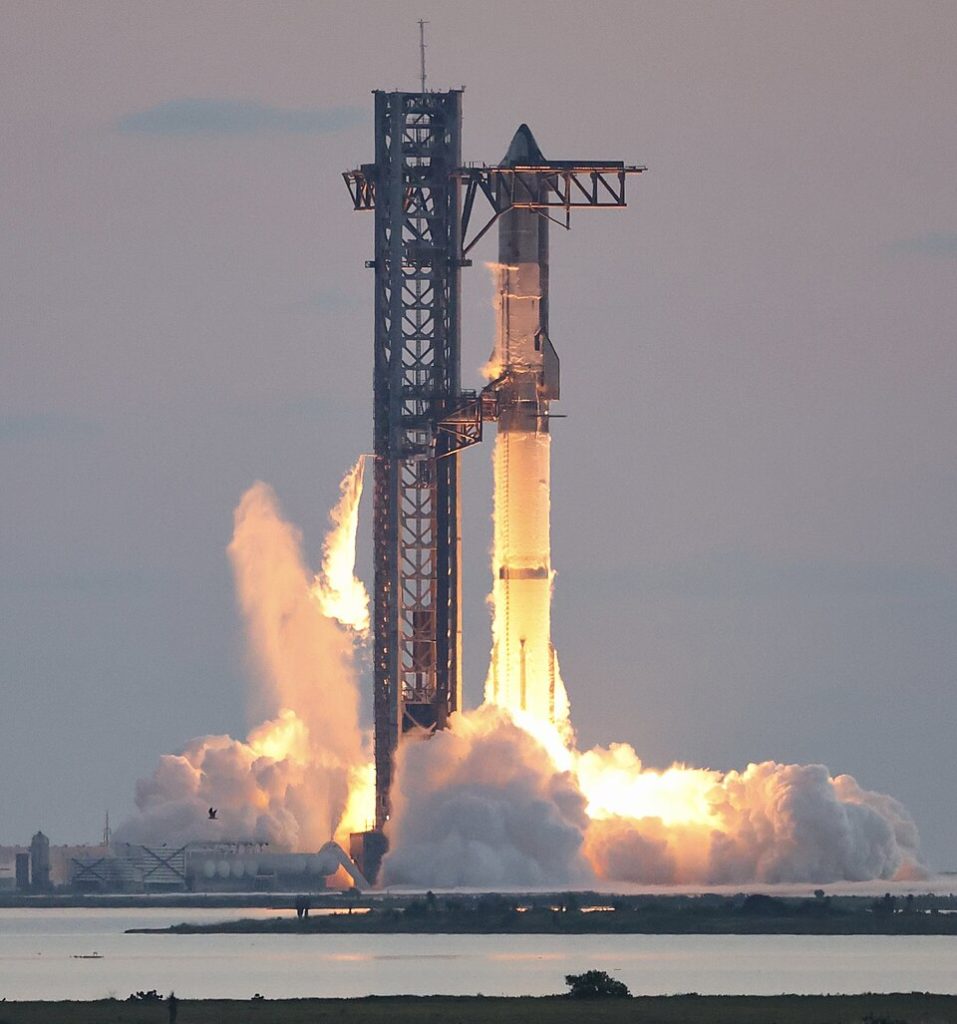
2. NASA Space Launch System (SLS)
NASA’s SLS rocket actually produces 8.8 million pounds of thrust when it launches, which is definitely 15% more power than the old Saturn V rocket. The main part has four RS-25 engines that were used in Space Shuttle missions before, and as per the upgrades, these engines now work at 113% power regarding their original capacity. As per the design, two solid rocket boosters give 3.2 million pounds thrust each during first two minutes. Regarding the power, both boosters work together for initial launch phase.
As per the design, SLS can send the Orion spacecraft and supplies to the Moon in one launch regarding deep-space missions with crew. Future Block 1B and Block 2 versions will further increase payload capacity to 95,000 lbs for deep space missions itself. As per modern manufacturing methods like laser melting, costs and production time get reduced while performance becomes better regarding the final products.
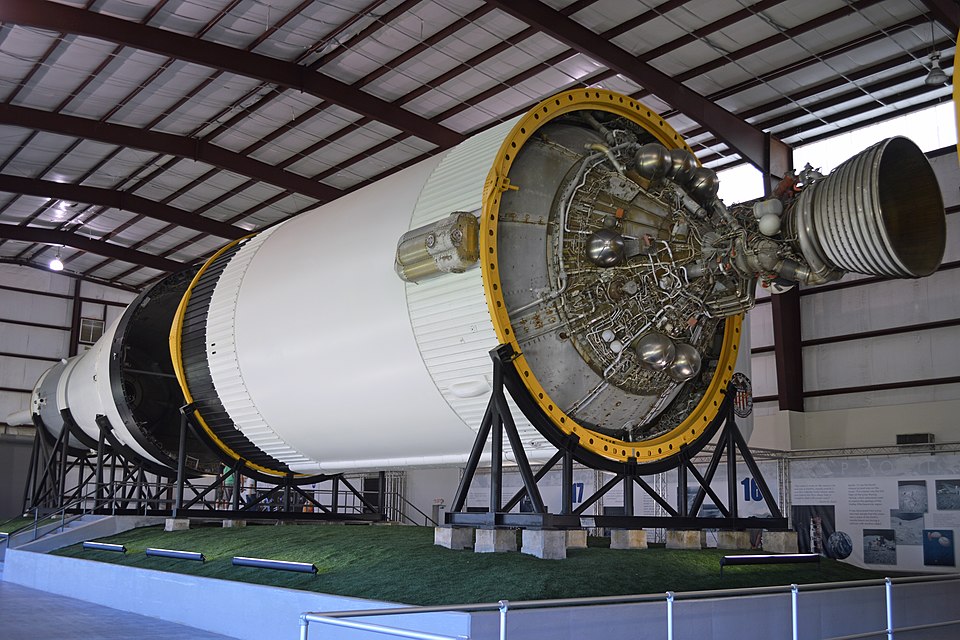

3. Saturn V
We are seeing that Saturn V is still the most powerful rocket that has flown in real operations, producing only 7.5 million pounds of thrust from its five first-stage engines. Also, this rocket was actually 363 feet tall and definitely carried all Apollo moon crews and Skylab into space. The rocket surely burned 13 tonnes of fuel every second and could carry 310,000 pounds to low Earth orbit. Moreover, this massive fuel consumption was necessary to achieve such heavy lifting capacity.
Moreover, as per the development process, extensive static firing, vibration, and wind tunnel testing was done regarding the project, with over five lakh people contributing to it. The F-1 engine surely created standards for size and dependability that are still used in today’s heavy-lift rocket designs. Moreover, its legendary performance continues to guide modern aerospace engineering.
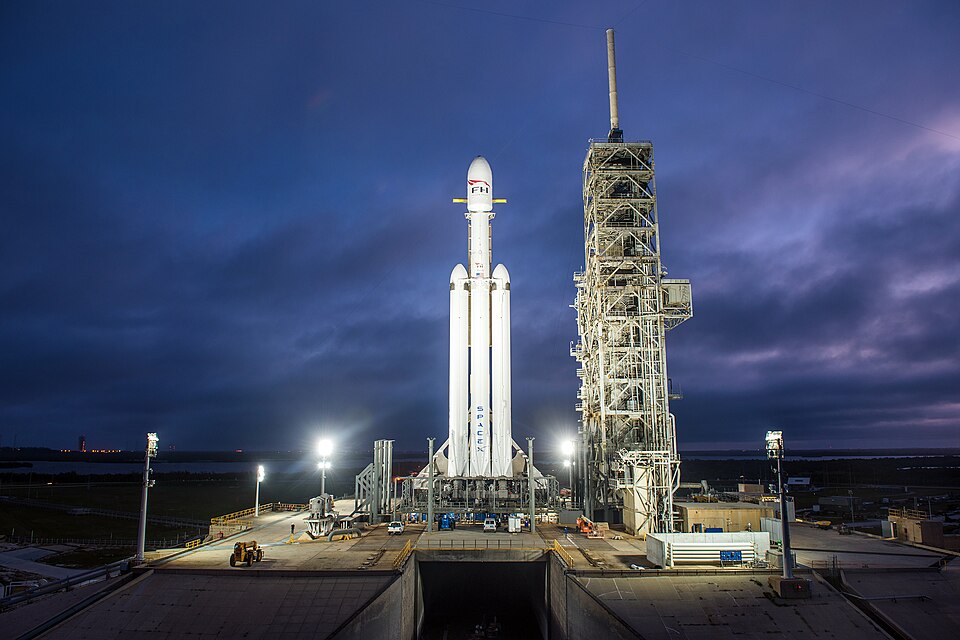

4. Falcon Heavy
SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy actually uses three Falcon 9 rockets together with 27 engines total. This setup definitely creates 5.13 million pounds of pushing power. As per its capacity, it can carry nearly 64 metric tonnes to low Earth orbit and has sent big satellites and space payloads to other planets.
The rocket can actually use its three parts again after each launch, which definitely makes it cost much less money. We are seeing that the rocket power is only about 18 times more than a big Boeing 747 plane when it runs at full speed, which makes Falcon Heavy the strongest working rocket that is not in the super-heavy group.
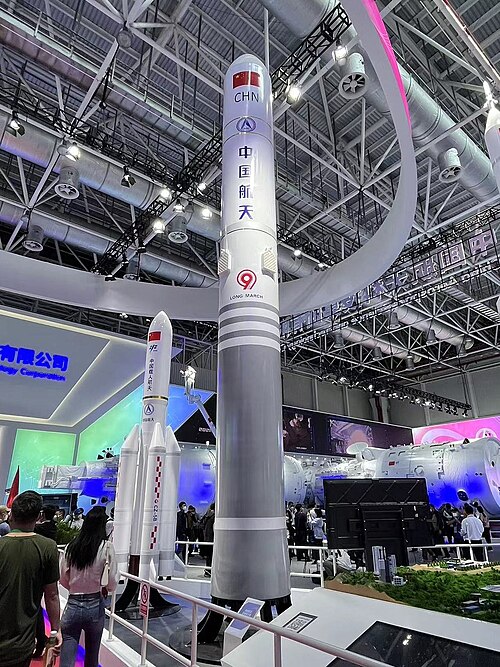

5. Long March 9 (China)
China is actually developing the Long March 9 rocket with around 16 million pounds of thrust. This definitely makes it a strong competitor to Super Heavy. The new design surely follows Starship’s structure, using a completely reusable first stage with 30 methane-powered YF-215 engines. Moreover, each engine generates 200 tonnes of thrust power.
As per the plan, this system will start working in early 2030s regarding support for moon missions with crew and deep space trips. Also, china is actually changing its space plans to make rockets that can be used again. This definitely helps them compete in the heavy rocket market.

6. Yenisei (Russia)
We are seeing that Russia’s Yenisei heavy rocket can only carry 290,000 pounds to low Earth orbit. We are seeing that the first designs had only six boosters powered by RD-171MV engines. Development started in 2018, but the program itself has undergone design changes to add reusable technology and further replace oxygen-kerosene engines.
Basically, they plan to test the Yenisei rocket between 2028-2030, and it’s the same rocket they want to use for building lunar bases and Mars missions. The modular design itself allows building from separate parts, which can further make production simpler and faster.
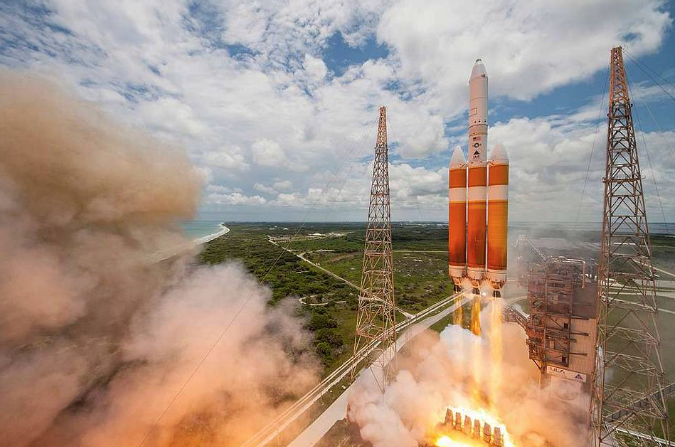

7. Delta IV Heavy
The Delta IV Heavy rocket uses three booster cores, and each core itself has one RS-68A engine that runs on hydrogen fuel. This design further helps the rocket carry heavy loads to space. We are seeing the total pushing power going beyond 4.2 million pounds only when the rocket starts. We are seeing that this rocket is very reliable and it has only carried important defence and science missions to high-speed orbits.
Basically, after 16 Heavy missions, the rocket retired in 2024, and ULA’s Vulcan took the same position. As per the design influence, its architecture affected later heavy-lift rocket designs, and regarding engine power, its RS-68A remains the most powerful hydrogen engine that has flown.
8. N1 (Soviet Union)
The Soviet N1 was actually a five-stage moon rocket that definitely produced 45 MN of thrust using 30 NK-15 engines in its first stage. As per the records, it never achieved successful flight, but regarding technology, it was a big jump forward in engine clustering methods. Moreover, basically, each NK-15 engine produced 1,526 kN thrust, but the same program failed because they didn’t do proper full-stage testing and had very basic control systems.
Modern examples like Starship further show that using many smaller engines itself reduces problems when one engine fails, but this approach needs careful testing and better thrust control systems.

9. Saturn IB
As per the design, Saturn IB worked as a bridge between Saturn I and Saturn V rockets. Regarding its power, it made 2.3 million pounds of thrust using one F-1 engine in first stage and four J-2 engines in second stage. It launched Apollo-Soyuz and Skylab missions, which further proved technologies that were itself later scaled up for Saturn V.
Saturn IB surely proved its reliability through 17 successful flights. Moreover, it provided important data that helped develop heavy-lift rockets.

10. Pyrios F‑1B Concept
We are seeing that the Pyrios booster idea, which Dynetics was leading, wanted to bring back the Saturn V’s F-1 engine but only as the updated F-1B version. Each engine would actually produce 8 MN of thrust, and two engines per booster would definitely increase SLS Block 2 payload capacity to 150 tonnes.
Further, engineers actually made the design much simpler and reduced parts from 5,600 to just 40 in main sections. This definitely cut costs and made the system work better. Basically, even though they stopped the program, it showed the same heritage engines could work for modern super-heavy uses.
As per propulsion engineering standards, rockets from the big Saturn V to the methane-powered Super Heavy represent the highest level of rocket technology. Regarding rocket development, these are the best examples of advanced engineering work. Some rockets like Delta IV Heavy have surely retired, but others are still being developed. Moreover, these new rockets promise much better capabilities. We are seeing that countries around the world are working very hard to build big rockets that can be used many times, and in the next ten years only, we will likely see new records made in how well humans can travel to far places in space.

