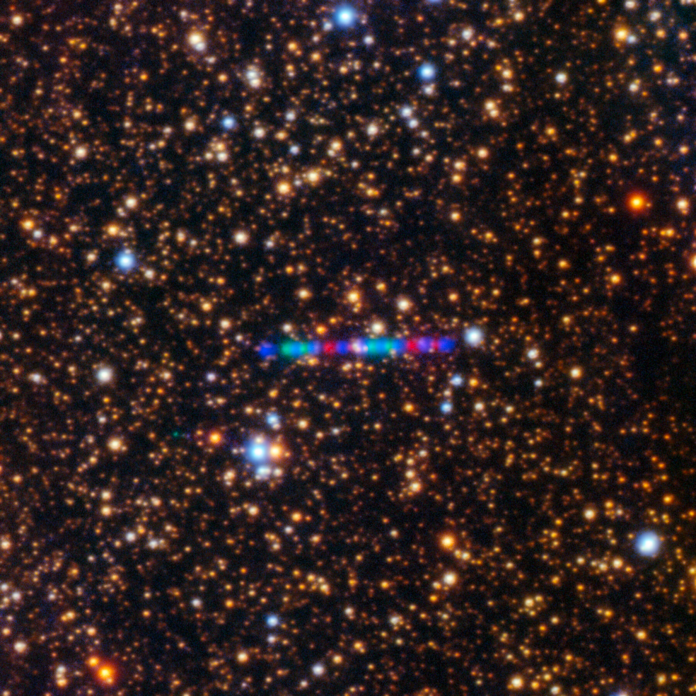
It’s not often that the whole planet has to unite to deal with a thing that predates even our solar system and to watch that thing ignore the laws of physics that apply to comets. This has happened with 3I/ATLAS, which ranks as the third known interstellar visitor. The joyous union that existed between various parties with regards to celestial data has created the most recent scandal.

1. The Interstellar Mystery with Unconventional Parameters
The traceback of the path for 3I/ATLAS confirms its origin is well beyond the solar system’s gravitational pull, likely within the last seven billion years in the galactic thick disk, contrasting prominently with non-gravity forces acting for the first time among few bodies, including 1I/ ‘Oumuamua. Contrary to standard cometary activity, which is defined by its constant antitail aimed directly at the sun, ‘jetting’ activity intensely oscillating over harmonic patterns, and thermal and ultraviolet emissions uncharacteristic of models designed for sublimation on icy surfaces. The Telescopio Twins, which are 2m in size and are situated in the island of Tenerife, matched the first two above-mentioned attributes with its rotational period of 14-17 hours, which is a very unusual observation for this type of interstellar comet.
2. Chemistry Beyond the Solar System Norm
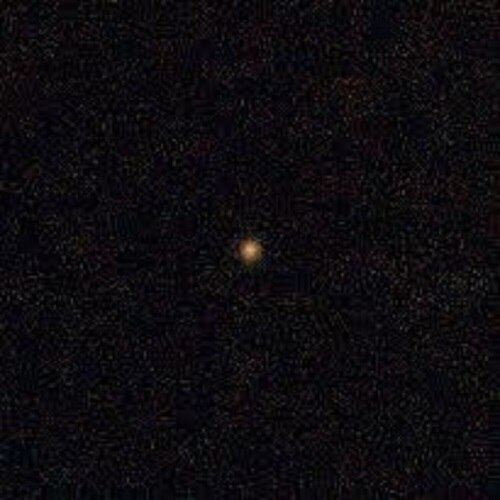
CO₂ was found eight times more concentrated in the coma than H₂O, which is a characteristic contrary to the composition margin in solar system comets. In my entire life, I’ve never observed a spectrum with a CO₂ feature so prominent in a comet. It’s a real first for the James Webb Space Telescope, said Martin Cordiner, a scientist at NASA Goddard. Then came the discovery at the Very Large Telescope, another wonder. The presence of nickel, but no iron, due to exotic chemical reactions like nickel tetracarbonyl. The unusual presence of elements points toward a formation region beyond the CO₂ ice line in this protoplanetary disk.
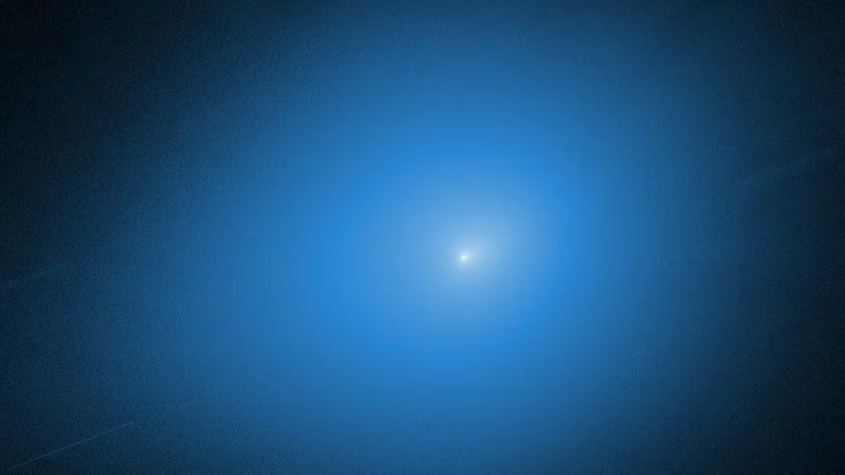

3. The Mechanics of Non-Gravitational Acceler
In comets, a corresponding acceleration might be caused by asymmetric outgassing or gas directions acting as a propulsion source. The size and corresponding direction of this force are dubious when matched with the level in the confrontation over 3I/ATLAS because all this data requires astrometry data in quick succession, and this is basically a level of information that has not been unreleased yet.
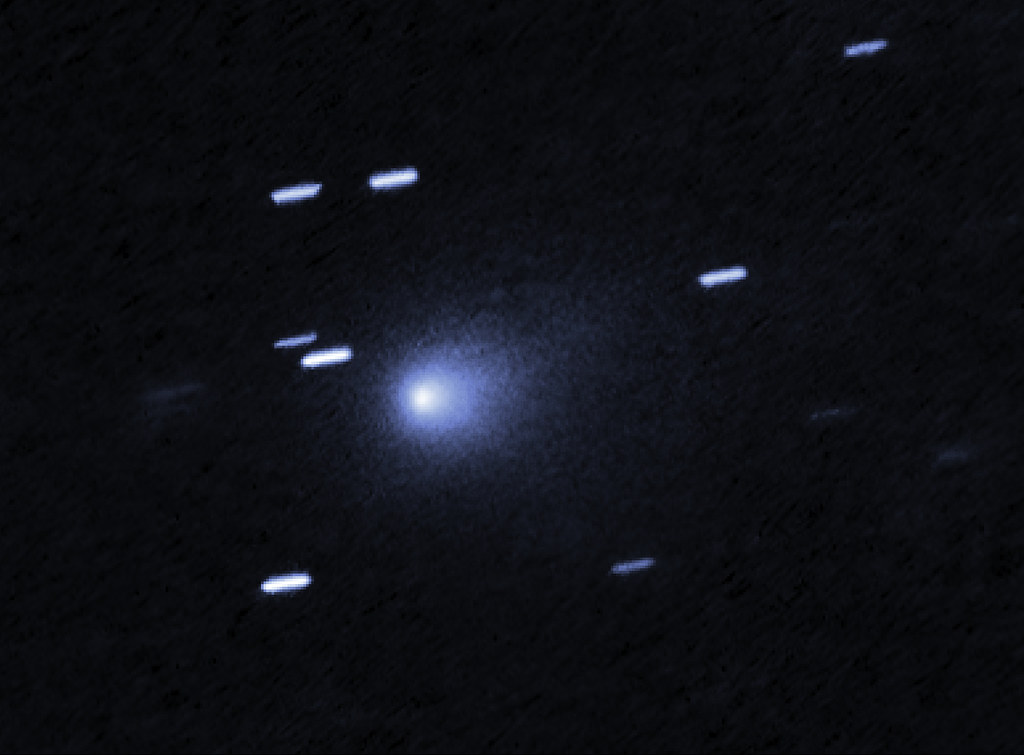

4. Planetary Defense Imperatives
3I/ATLAS’ close approaches: October 2025 close approach of Mars, November 2025 close approach of Venus, December 2025 close approach of Earth, and March 2026 close approach of Jupiter, brings with it the historic opportunity to enhance the models for the gravitational perturbations. Anomalous asteroids will be the target of the current planetary defense strategy, where it is expected to test the simulation of the threshold of discovery and the likelihood of impact. The NEO Surveyor mission, the Flyeye telescope, and The Vera C Rubin Observatory are meant to find anomalous asteroids sooner, and this would necessitate that all data for past anomalous asteroid cases be obtained.

5. A Pattern of Withholding Data
Despite the scientific significance of the object, only processed joint images and reports with a delay have been made accessible by NASA. This contrasts with the availability of information regarding the selected targets with lower anomalies. It also connects to the controversy surrounding the cataloging of asteroids by NASA known as the asteroid survey, or the NEOWISE asteroid survey. This was because the protracted battle by physicist Nathan Myhrvold, via the Freedom Of Information Act, implied the resistance by the agency to provide the information.

6. Legal Channels for Transparency
Under FOIA, records must be released unless they fall under various exemption clauses. Deliberative process or contractor records exemptions qualify in a contestable manner with regard to matters of public protection and defense of the planet, as related to space science. Lawsuits may be brought to mandate judicial review of exempt information, but plaintiffs must subsequently demonstrate their standing on grounds of scientific, professional, or public safety issues, which might put astronomers, Planetary Defense professionals, or investigative journalists qualified.

7. The Cost of Silence to Science
One of the most renowned astrophysicists at Harvard, Avi Loeb, has repeatedly emphasized the fact that the existence of Interstellar objects is the new type of data available in the field of astronomy and may provide some answers regarding the chemistry and mechanics of other star systems. Without the availability of data, replication and falsification are not possible, and it becomes absolutely irrelevant globally when it comes to projects and networks, including the International Asteroid Warning Network.
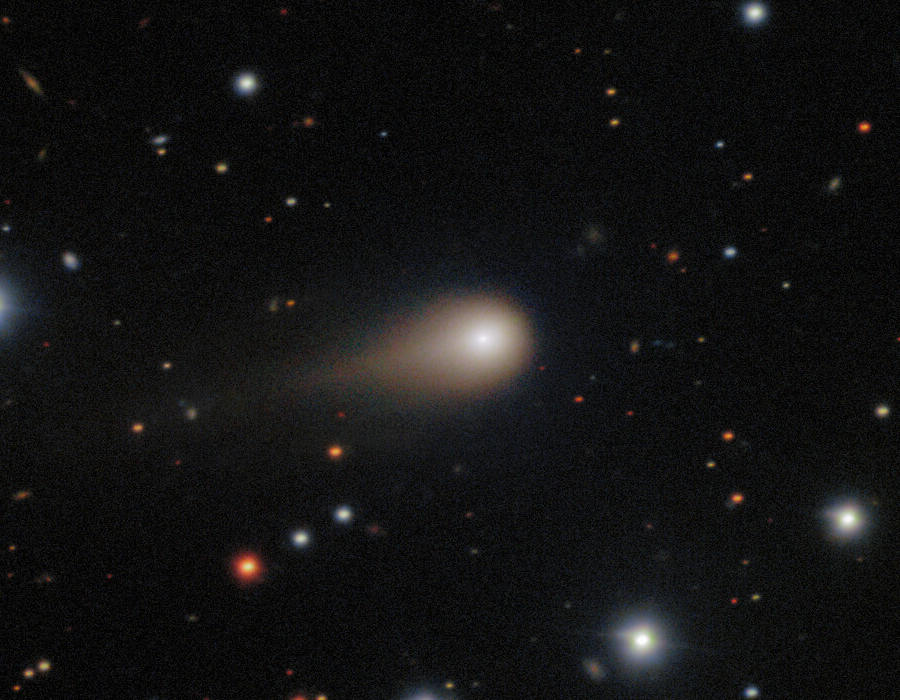

8. A Narrowing Observational Window
3I/ATLAS will be occulted from view on Earth during its perihelion because of the glare, but only orbiting or Mars-based observatories will offer the chance to see the comet. With the end of 2026 looming, it will be too faint for viewing from Earth. It is urgent each day diminishes the advantage of this unprecedented encounter by not issuing the data release promptly so that the maximum advantage of this encounter for point-one-one-one-one-one A D E/M E will be obtained.
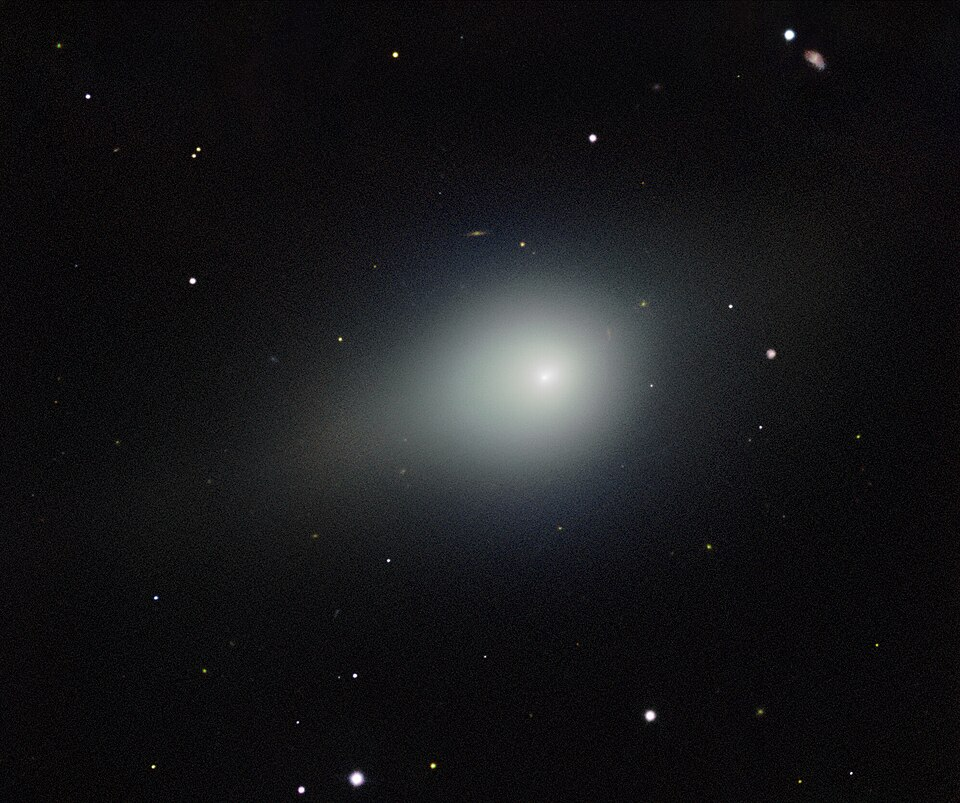

The harder the comet enters the darkness, the more the question would not only be what the comet is but if the institutions who are supposed to understand the comet will allow the world to see the truth in time.


