It is nothing but audacious how Tesla is valued going into 2026. With a P/E of more than 300 and a market capitalization hovering around $1.6 trillion, the company stands at the juncture of extreme optimism on the part of investors and equally extreme execution risk. The narrative of this valuation has begun to shift from deliveries of vehicles to autonomy, robotics, and AI-enabled services-a transformation that could definitely redefine its revenue model but is fraught with regulatory and technical hurdles.
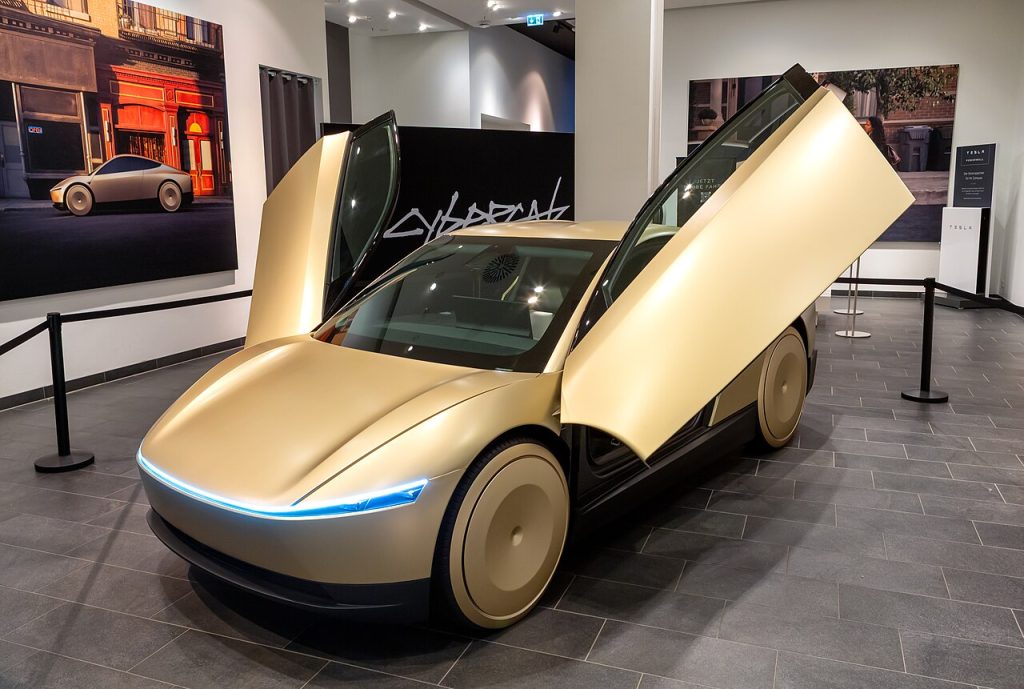

1. Cybercab: Engineering for Driverless Mobility
Tesla will start producing the Cybercab in April 2026 from its Austin plant. This purpose-built autonomous EV does away with pedals, steering wheels, and side mirrors in its quest to have the lowest cost-per-mile for robotaxi duty cycles. Elon Musk has boasted of a 10-second manufacturing cycle time, a near fourfold advance over the one-minute cycle of the Model Y, which theoretically should allow production of 2–3 million units per year. However, such vehicles are not road-legal without federal exemptions. Similarly positioned Amazon-backed Zoox and GM’s Cruise Origin face similar delays, highlighting that engineering progress is very much at the mercy of regulators.

2. Regulatory Roadblocks to Autonomy
The regulatory framework at the federal level in the U.S. remains fragmented, with federal regulators deferring the process of rulemaking to states. Approvals are granted on an uneven basis, with Tesla just this summer starting unsupervised robotaxi rides in Austin. Expanding to cities including Houston, Miami, and Las Vegas depends on formal exemptions. Oppenheimer projects modest earnings potential from autonomy through 2030-$1-$3 EPS-said regulatory bottlenecks and incremental validation required for each new functionality.
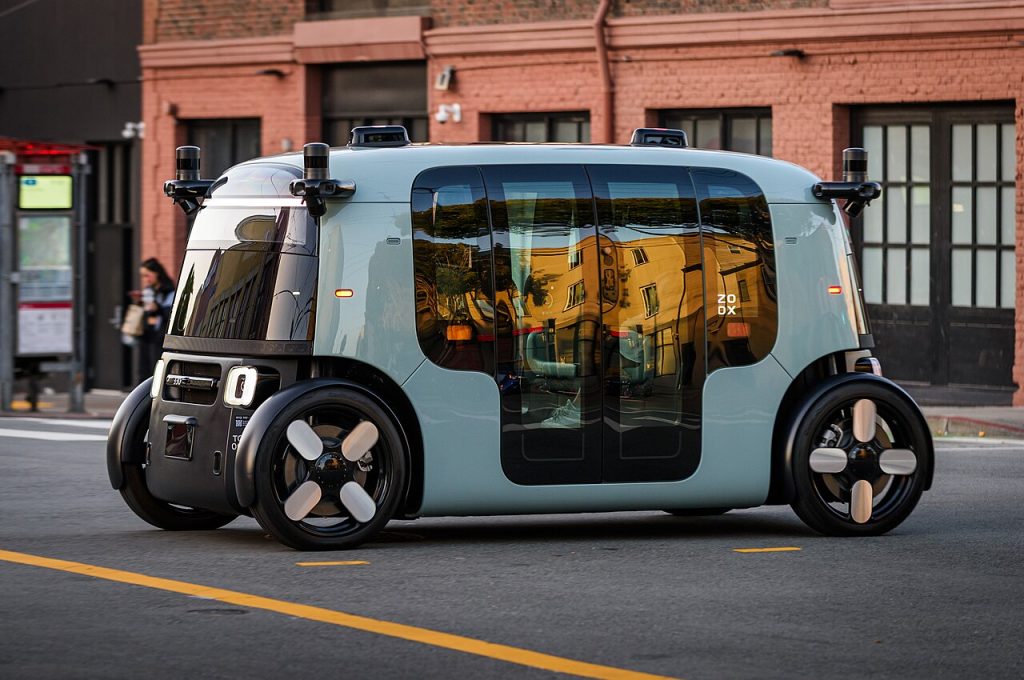

3. Robotaxi Economics and Scaling Challenges
Tesla’s robotaxi model is predicated on high utilization rates and low operating costs. Deutsche Bank analysts see the fleet scaling from 152 units to over 2,500 by mid-2026, but profitability depends on rapid deployment and software-hardware integration. Goldman Sachs stresses that “the key focus from here will be how fast Tesla can scale driverless operations.” On a value capture of $0.79 per mile and at 60% utilization, Oppenheimer estimates $2.25–$3.22 EPS per 250,000 vehicles figures that shrink under competitive pricing pressure.
4. AI Hardware Roadmap
Tesla’s AI chip strategy underpins its autonomy ambitions. The AI5 chip, developed under a $16.5 billion partnership, reaches limited production in 2026 and AI6 in 2028. AI6 has the potential to unlock 1:12 operator-to-robotaxi ratios while reducing labor costs from $120,000 to $10,000 per vehicle annually. Musk has also thrown out the idea of constructing a “gigantic chip fab” in Texas and monetizing idle vehicles as distributed compute nodes, offering owners $100–$200 a month-a potential new revenue stream if technical and economic feasibility can align.
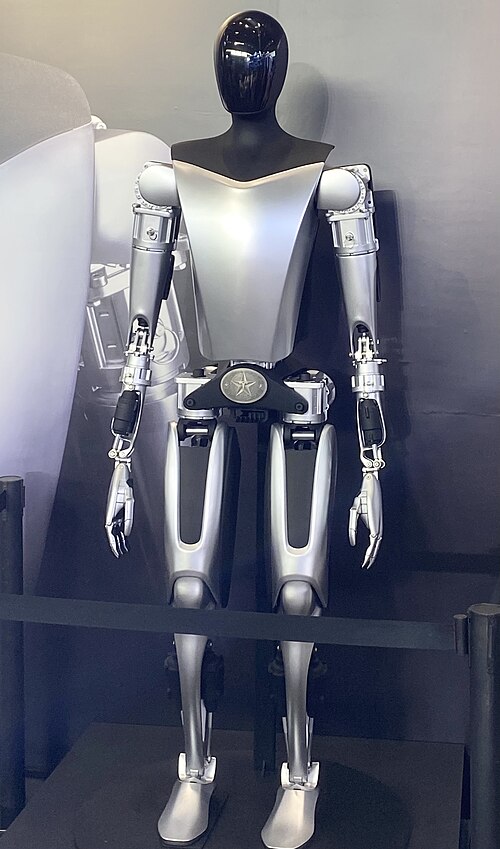
5. Optimus: Humanoid Robotics as a Growth Pillar
The Optimus humanoid robot, due possibly as early as 2026, is positioned as a long-term disruptor in physical-service industries. Musk recently declared that it might become “the biggest product of all time,” outselling smartphones. Tasks range from industrial automation to domestic chores, leveraging Tesla’s AI and sensor stack.

Competitors such as Boston Dynamics and 1X are advancing dexterity and AI integration, but practical adoption will depend on cost, reliability, and regulatory acceptance in workplace environments.
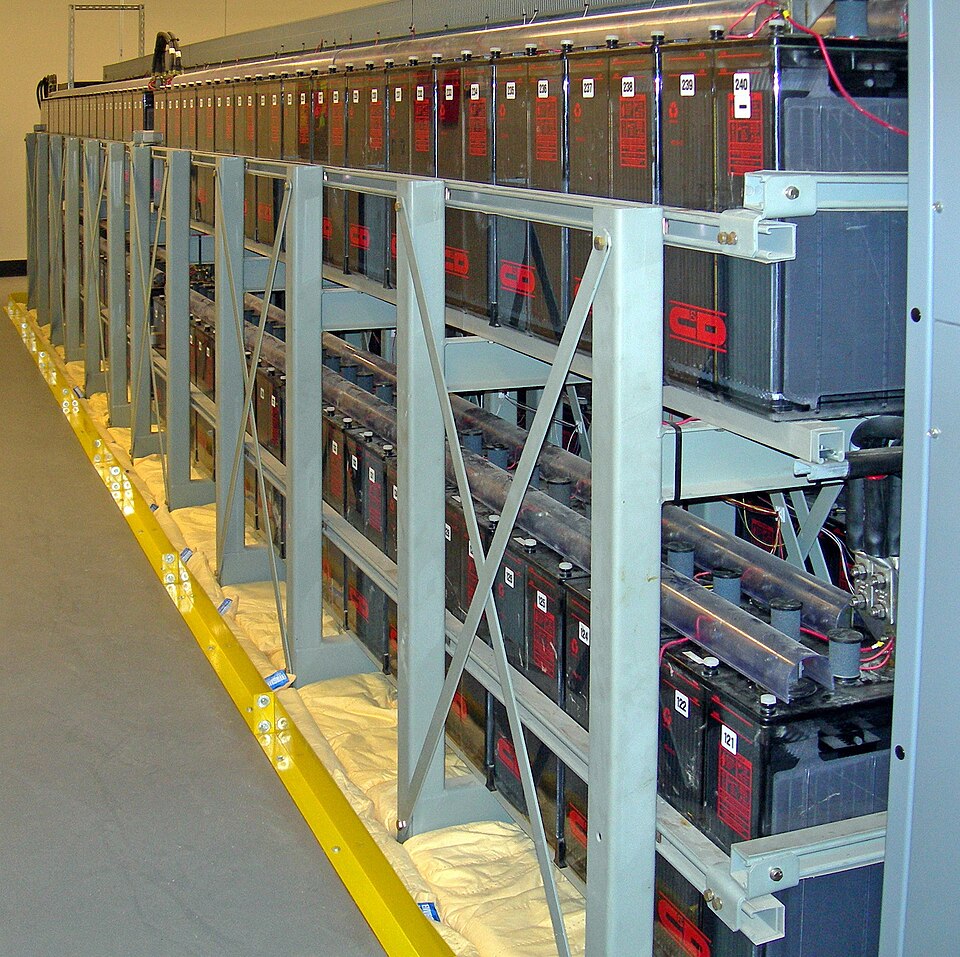

6. Energy Storage: The Segment That Isn’t Touted Enough
Tesla’s energy business is turning out to be a big contributor to earnings. Energy generation and storage revenues jumped 67% in 2024 to more than $10 billion as gross margins topped 30% in 2025. Products like the Megapack-already in its third incarnation, the Megablock configuration-offer 248 MWh AC-per-acre density. Megapack 4 incorporates substation functionality, outputting directly at 35kV to cut deployment complexity. AI data centers and utilities are driving demand, while tariffs on Chinese-sourced battery cells remain a margin headwind.

7. Valuation Tensions and Market Psychology
Tesla’s stock is up about 120% since April 2025, fueled by autonomy hype despite declining automotive margins. The market cap is “ridiculously overvalued,” critics such as Michael Burry claim, noting the net income of $5.1 billion against a $1.35 trillion valuation. Bulls say Tesla merits its premium for vertical AI integration and diversified growth levers. Price targets range from $19 to $600, reflecting deep polarization.

The average Wall Street target is near $384, suggesting a possible downside if autonomy and robotics don’t scale as anticipated. Success for Tesla in 2026 means translating technological ambition into operational scale. The production ramp-up of Cybercab, deployment of robotaxi, rollout of AI hardware, and commercialization of Optimus all pose different execution challenges. And for investors, this stock already values in extreme success on all fronts, leaving little margin for error for what could be a year that would redefine Tesla.


