But what if the most underappreciated element in the electric vehicle revolution isn’t the battery itself, but rather the box and packaging it comes in? The global battery packaging market, estimated to be valued at USD 31.96 billion in 2023, is projected to jump to USD 84.83 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 11.57%, driven by the electrification of transport, renewable energy storage build‑out, and the relentless push for safer, lighter, and more sustainable designs. Beneath that growth lies a convergence of advanced materials science, thermal engineering, and regulatory pressure that is reshaping how energy storage systems are protected, cooled, and recycled.

1. EV Adoption and Energy Storage Drive Demand
Electric vehicles and grid‑scale storage today are the main driving forces behind packaging innovation. Lithium‑ion packs for EVs require casing solutions that are lightweight yet mechanically robust, featuring integrated thermal management to prevent thermal runaway. In Asia‑Pacific, where 96% of all EVs sold are battery electric, manufacturers like BYD, CATL, and LG Energy Solution are ramping up production of prismatic and cylindrical cells, driving suppliers to high‑volume, precision‑engineered packaging capable of supporting high energy densities and a wide range of form factors.

2. Thermal Management Becomes a Core Design Function
Packaging is no longer passive protection; it’s an active thermal control system. Aluminium housings can be extruded with complex cooling channels, while high‑silicon steels offer superior fire resistance, withstanding over 1000°C for 20 minutes without structural collapse, compared to aluminium’s 610°C melting point reached in seconds. Advanced designs incorporate phase‑change materials, heat‑dissipating coatings, and airflow‑directing septa that maintain optimal cell temperatures under fast charging and high‑load conditions.

3. Material Innovation Targets Weight, Safety, and Sustainability
With its corrosion resistance and recyclability—re‑melting consumes just 5% of the energy of primary production aluminium remains dominant, yet steel is regaining ground with thinner high‑strength alloys cutting cost by up to 50% for a 70 kWh pack. Composite thermoplastics, reinforced with glass fibres, are breaking into mid‑market EVs, offering 20% weight reduction versus aluminium, plus corrosion immunity, integrated flame retardancy and design freedom for complex geometries. Multi‑material “sandwich” structures are being prototyped in pursuit of combining stiffness, thermal isolation and EMI shielding in a single moulded component.
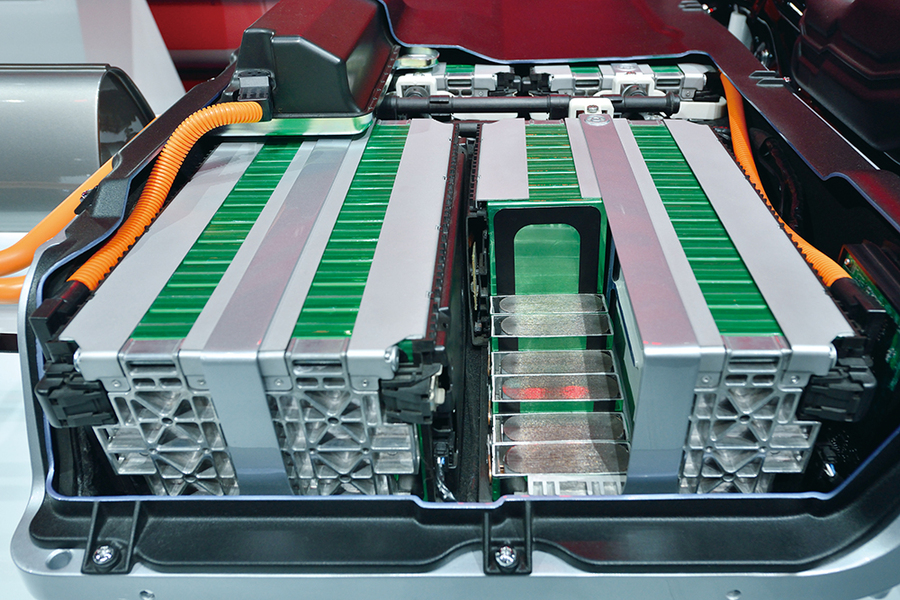
4. Regulatory and ESG Pressures Accelerate Change
OEMs are being driven toward recyclable and biodegradable packaging by Europe’s Green Deal and end‑of‑life vehicle directives. Federal safety standards and incentives for domestic battery manufacturing in the U.S. are accelerating the pace of adoption for recyclable casings and modular pack designs. Asia‑Pacific’s dominance is further cemented with 41.28% of the revenue share in global packaging in 2023, driven by China’s vertically integrated supply chain and India’s projected 90% growth in EV battery pack output through 2029, both aligned to circular economy targets.

5. Solid-State and Next-Gen Chemistries Redefine Requirements
For all-solid-state batteries with higher energy densities and different thermal profiles, packaging requires increased insulation, tighter tolerances, and new sealing technologies to protect solid electrolytes from moisture ingress. Suppliers are developing flame-resistant films such as Covestro’s Makrofol EC, and acrylic adhesives like Trinseo’s LIGOS A Series to meet emerging demands.

6. Corrugated and Cardboard Solutions Dominate Transport
About 74.14% of revenue share is held by corrugated packaging for shipping and storage, with innovations like fire-resistant coatings and custom inserts from Smurfit Kappa and DS Smith. Cardboard, with 61.23% revenue in 2023, is seeing developments such as heat-resistant, modular designs for small-format lithium-ion cells, balancing cost, recyclability, and protection.
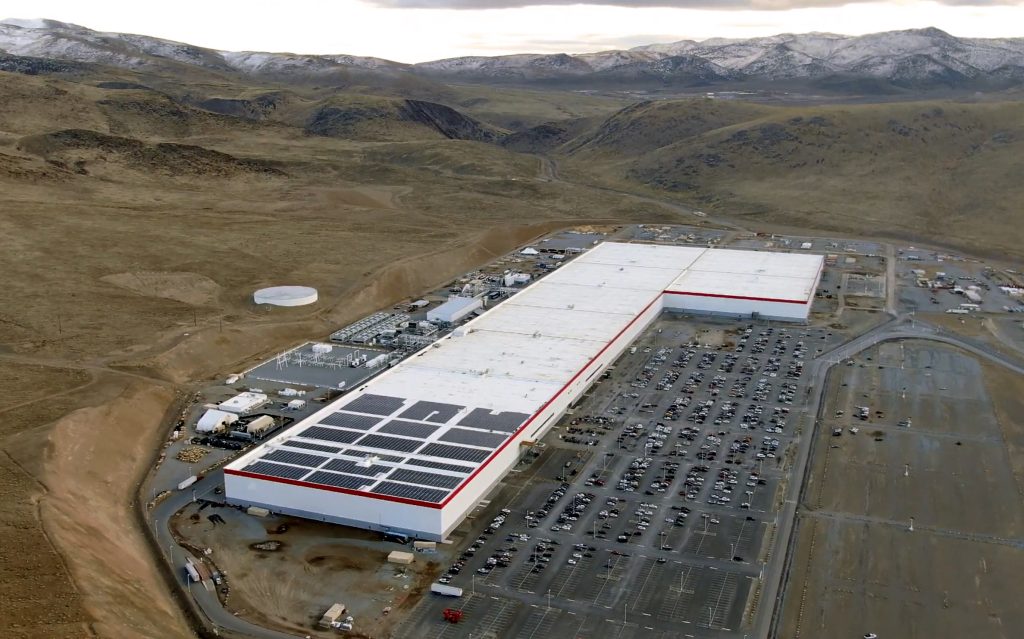

7. Integration of Smart Manufacturing and Automation
Gigafactory‑scale production is driving automation in packaging lines. Industry 4.0 tools, such as AI‑based quality inspection, digital twins, and predictive maintenance, have been deployed to ensure repeatability while reducing scrap. Thermoplastic moulding, with cycle times below 120 seconds, allows high‑volume production of large enclosures without major capital retooling, while providing options for embedded sensors for temperature and impact monitoring.

8. Biodegradable and Bio‑Inspired Packaging Materials
Research on biodegradable casings and separators based on soy protein isolate, wool, and algae‑derived cellulose is moving from the laboratory to pilot scale. These materials provide ionic conductivities above 5 mS cm⁻¹ with lithium transference numbers up to 0.77, ensuring performance thresholds are met under reduced end‑of‑life waste. Bio‑inspired designs begin to appear, emulating natural structures for strength and thermal stability in both EV and consumer electronics applications.
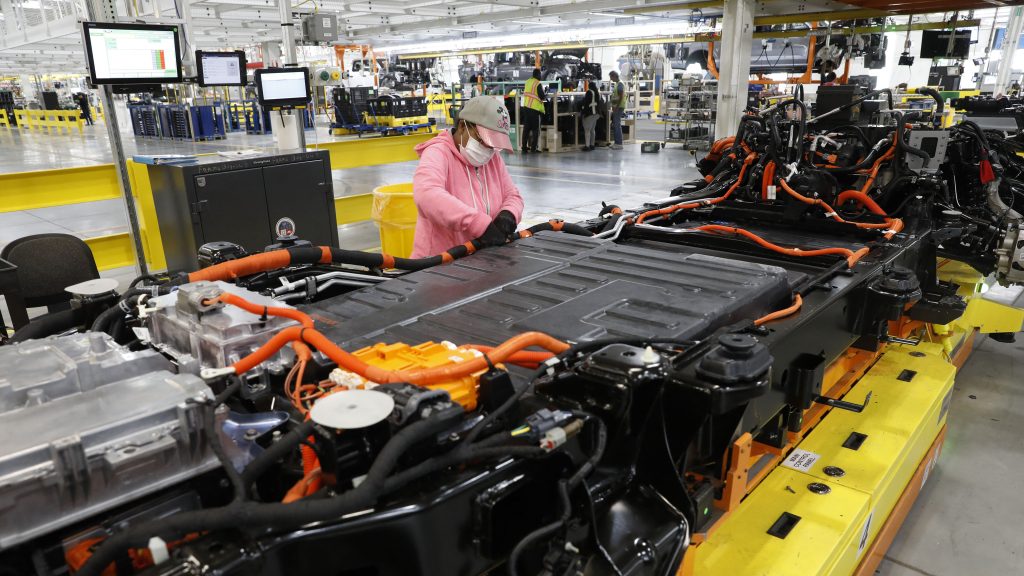

9. Regional Growth Hotspots
The Asia‑Pacific region leads in volume and innovation, with China retaining 87% of the regional EV battery pack market and Japan and South Korea working on high‑performance chemistries. Europe’s growth at a 13.83% CAGR is driven by Northvolt and others providing recyclable solutions for both lithium‑ion and solid‑state cells. North America’s growth is anchored by Tesla, Panasonic, and LG Chem’s domestic manufacturing, while the U.S. is projected to reach USD 10.11 billion by 2032. With deepening EV penetration, scaling renewable energy storage, and persisting consumer electronics demand, battery packaging is turning into a high-tech, high-value segment of the energy storage supply chain. Material science breakthroughs, regulatory alignment, and manufacturing innovation are converging to make packaging a decisive factor in performance, safety, and sustainability.


