What does a $1.6 billion contract really buy in the world of military aviation? In this case, Pratt & Whitney’s latest award from the US Navy buys a multi-year guarantee that the beating heart of the F-35 Lightning II, the F135 engine, will remain mission-ready across the sprawling global fleet.
The agreement comes at a very critical time for the Joint Strike Fighter program. With more than 990 aircraft delivered and over 3,000 projected worldwide, the sustainment burden is high. It’s not just about spares; it’s about ensuring operational predictability, integrating future upgrades, and maintaining the propulsion edge against near-peer competitors.
This deal has extra value for both the defense watcher and the industry investor alike, given its signaling about where the Pentagon is placing its long-term bets in fighter sustainment and how Pratt & Whitney positions itself in a high-stakes race to modernize propulsion technology while keeping costs under control.
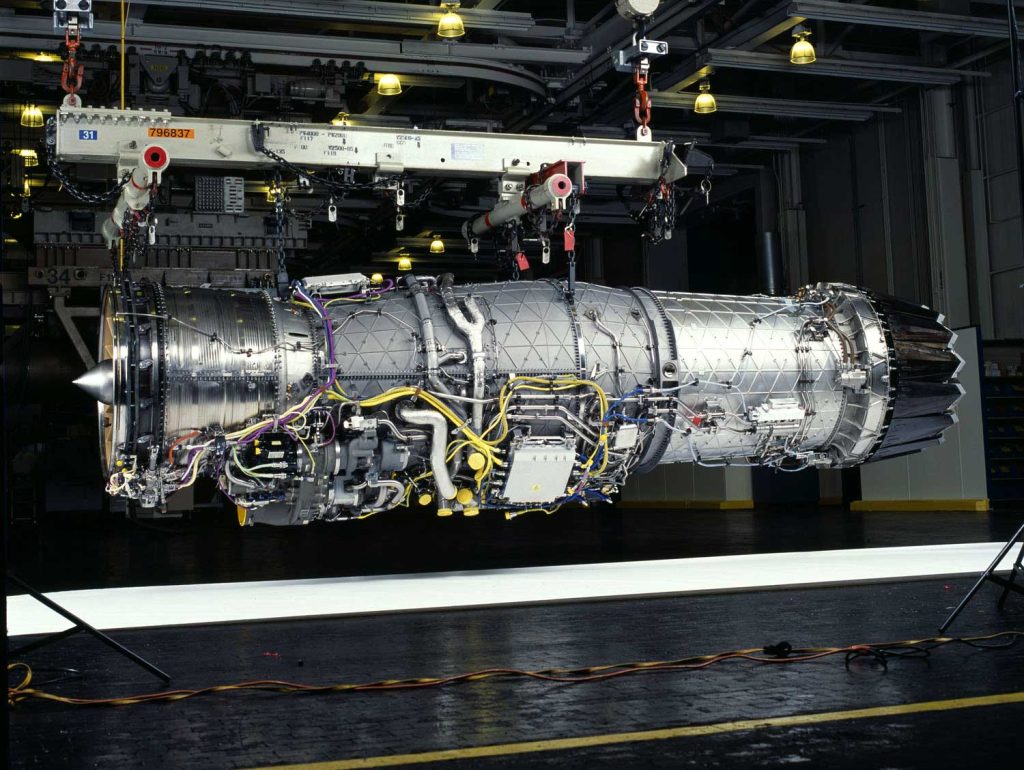
1. Scope of the $1.6 Billion Sustainment Package
The undefinitized contract is estimated at as much as $1,606,190,091 and provides for recurring sustainment support, to include program management, propulsion integration, replenishment spares, engineering services, and depot-level maintenance for all delivered F135 engines. Work locations range from East Hartford, Conn., to Brekstad, Norway, and Iwakuni, Japan. Work is expected to be completed by November 2026. This breadth reflects a truly global sustainment footprint designed to keep all three F-35 variants operational.

2. Supporting All Variants and Allies
This award is a package for all three variants, F-35A, F-35B, and F-35C, to achieve commonality across all U.S. services and partner nations. The Navy will make sure interoperability and mutual readiness standards are upheld for the associated allied fleets. This supports the F-35 Global Spares Pool in replenishing parts for more than 860 aircraft in 16 countries, keeping logistics pipelines in sync across borders.

3. Depot Repairs and Predictive Maintenance
The scope of the contract will include, but not be limited to, depot-level overhauls, hot-section replacements, and fuel and lubrication system servicing beyond routine servicing. Digital health monitoring will be applied to predict and prevent the failure of key components. Borescope inspections will assess the state of turbine wear. Integrating diagnostics into the sustainment model extends time on-wing and reduces costly engine removals, which have a direct impact on fleet availability rates.
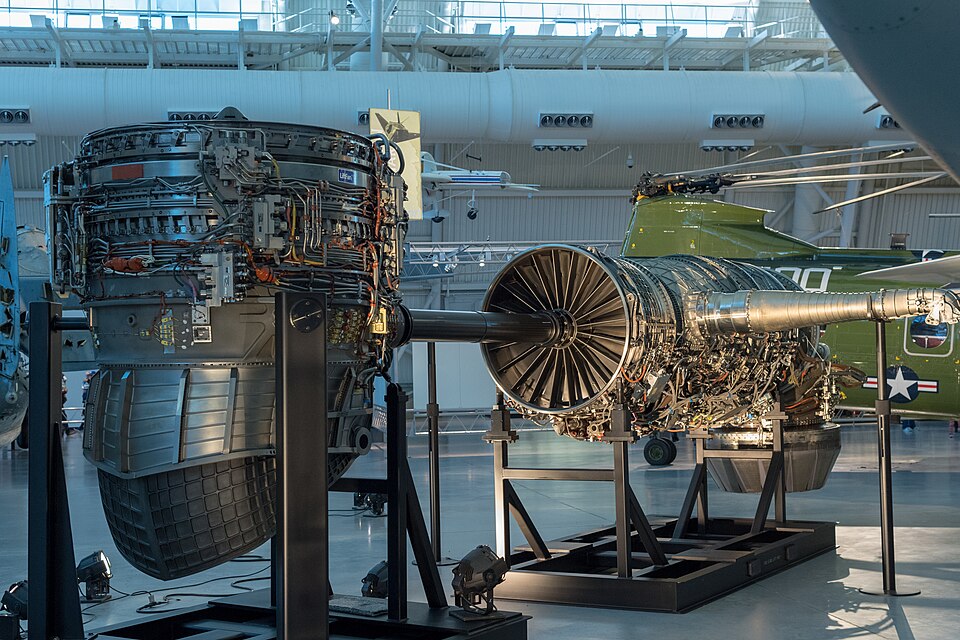
4. Strategic value for Pratt & Whitney
The deal secures a steady revenue stream for Pratt & Whitney and cements its place as the cornerstone in F-35 propulsion. This allows valuable operational data to flow from the field to feed into designs, both for the recent and impending Engine Core Upgrade program. The sustainment under such control bolsters Pratt’s leverage going into upcoming phases of modernization.

5. Core Upgrade and Block 4 Readiness
Now past its preliminary design review, the ECU is targeted at overcoming the F-35’s chronic cooling deficit and unlocking power-hungry Block 4 systems. Pratt hopes to field the ECU in 2029, although GAO estimates 2032. The upgrade ups the thrust, improves fuel efficiency and engine life, and is compatible with all variants-a critical consideration in the aftermath of the Pentagon’s dismissal of an alternative new-engine offering.

6. Mid-2020s Sustainment Cost Spike
Pratt executives have warned of a mid-decade rise in sustainment costs as the first wave of F135 engines reaches 2,000 flight hours and enters scheduled overhaul. That coincides with the Pentagon’s drive to get the F-35’s cost per flight hour down to $25,000. Depot backlogs, unexpected wear from harsh operating environments, and the slow rollout of upgraded rotor blade coatings all threaten to keep costs high; it may be 2030 before the fleet is retrofitted.

7. Supply Chain Visibility and DLA’s Role
The DLA has been expanding its role in F-35 sustainment through cataloging high-demand parts, managing regional warehouses, and integrating with the U.S. Transportation Command for global shipments. This move toward organic government oversight of the supply chain should enable better transparency, performance metrics, and resilience in contested environments in the run-up to the transfer of sustainment responsibilities to the services in 2027.

8. Aligning Sustainment with Readiness Targets
Those mission-capable rates today are 51.9% for the F-35A, 59.7% for the F-35B, and 61.9% for the F-35C, which is below service goals. Sustainment contracts like this are designed to close that gap by ensuring parts availability, reducing overhaul frequency, and integrating engineering upgrades. The priority on propulsion readiness is underlined by the Navy’s decision to decouple engine sustainment from airframe procurement.
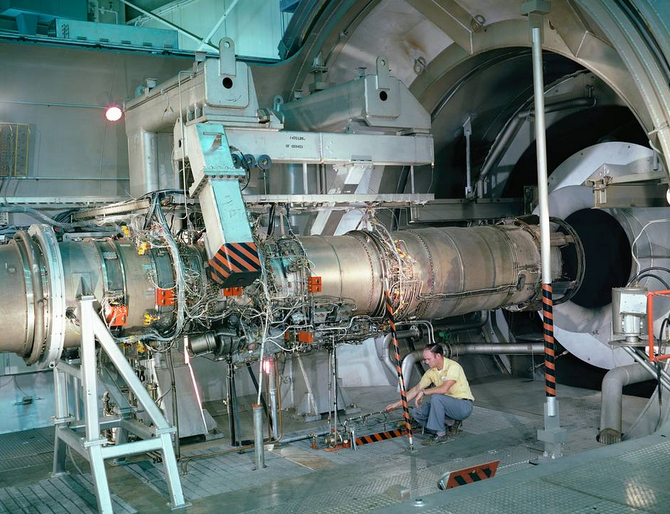
9. Positioning for Future Fighter Programs
While executing F135 sustainment and ECU, Pratt also competitively contends in the Next Generation Adaptive Propulsion program for the Air Force’s future air dominance platform. Lessons learned from managing the propulsion challenges of the F-35-particularly in cooling, lifecycle cost control, and global logistics-will inform its competitive standing in the sixth-generation fighter arena. This $1.6 billion sustainment award is more than a maintenance contract; it’s a strategic investment in the F-35’s operational future.
By locking in global support for the F135 engine, integrating predictive maintenance, and aligning with upcoming propulsion upgrades, Pratt & Whitney and the Navy ensure that the Lightning II remains combat ready while setting the stage for the next era of fighter propulsion technology.


