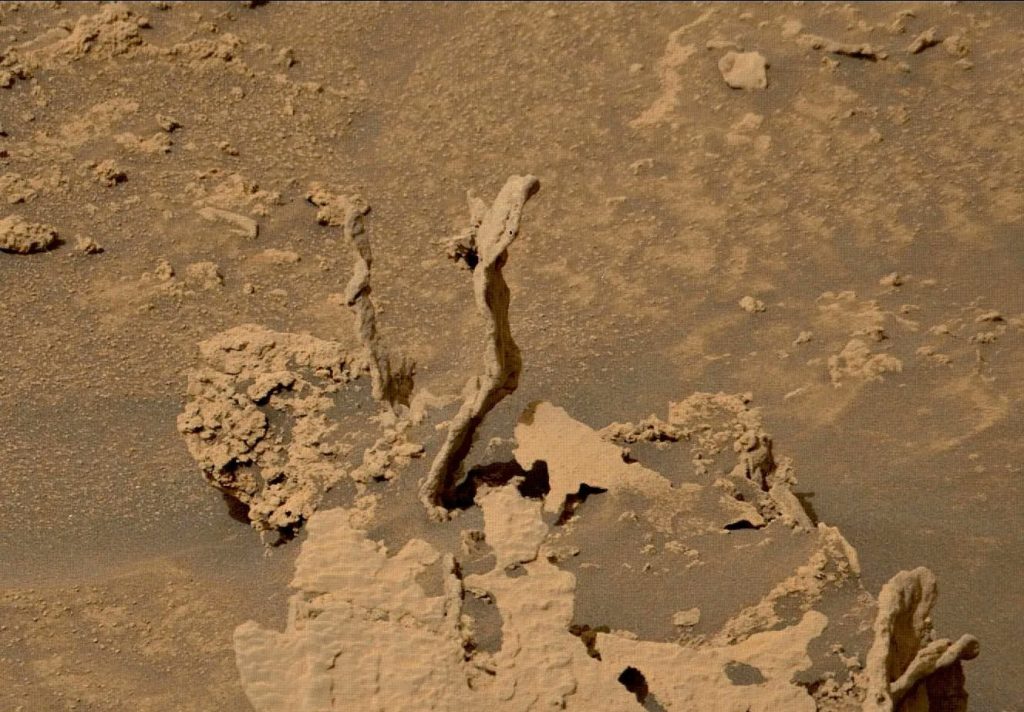
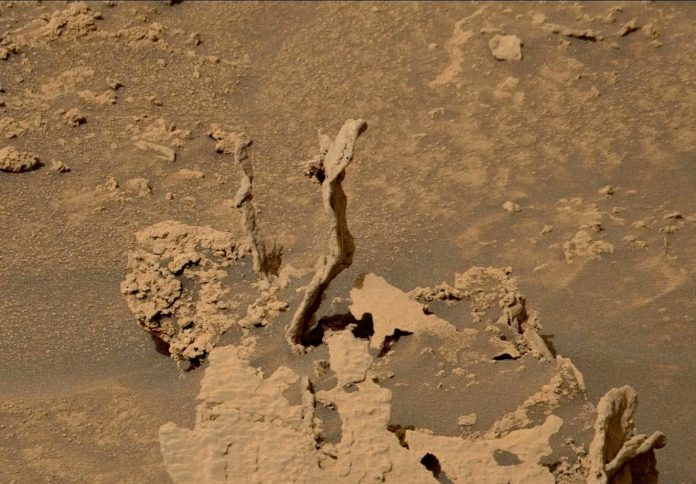
Is it conceivable that Mars, a planet heretofore regarded as barren and lifeless, contains landscapes so bizarre they cannot be explained easily? The Red Planet, for so long the fascination of astronomers and fantasists alike, still provides a procession of visual enigmas and geological wonders. Every new photo transmitted by orbiters and rovers seems to open up as many questions as answers, sparking arguments over the history of Marsand our own penchant for perceiving the familiar in the strange.
With each expedition, scientists discover more objects and patterns on Mars that appear to just shouldn’t be there on a barren planet. Some are the product of Martian geological processes, and others fool the human mind, imagining faces, animals, and even ruins of cities in rocks and dust. This article discusses seven of the most intriguing and mystifying Martian featureseach a reminder of the planet’s active past and to humanity’s ever-insatiable curiosity.
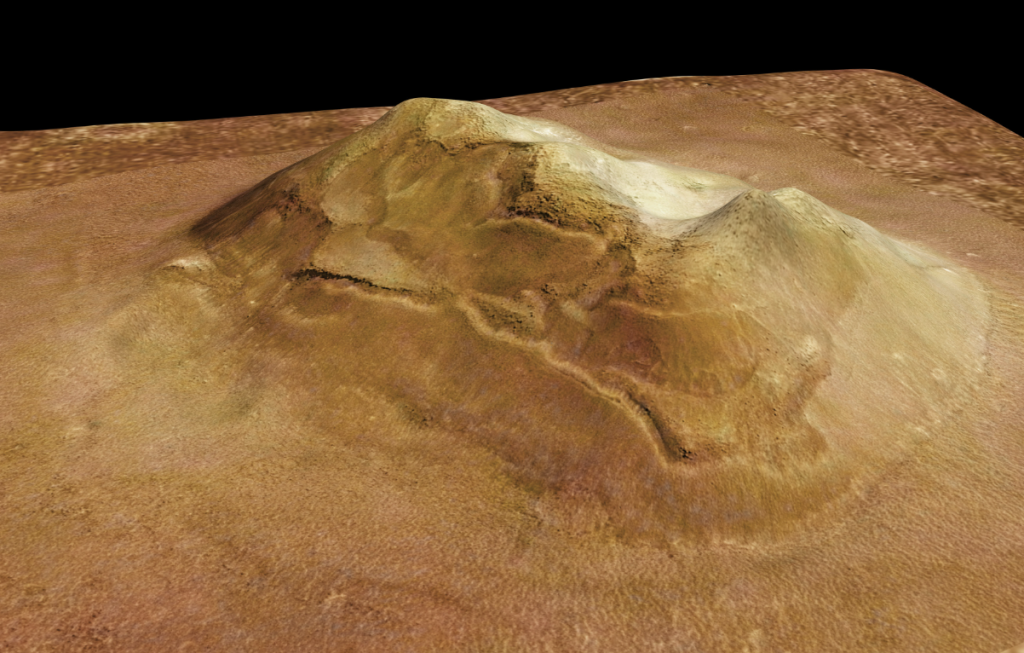
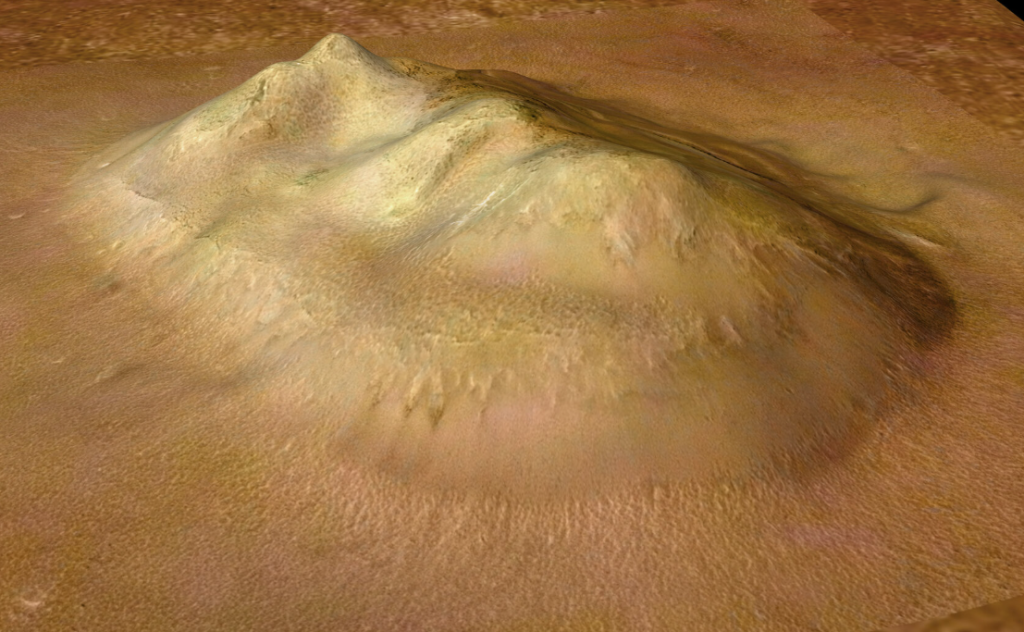
1. The Teddy Bear’s Face: Pareidolia on a Planetary Scale
When NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter snapped a photo in December 2022, the world went wild speculating about what seemed to be a gigantic teddy bear smiling up at it from Mars’ surface. The University of Arizona’s Lunar and Planetary Laboratory said that the face of the bear consists of a V-shaped nose collapse structure, two craters for eyes, and a ring fracture pattern defining the head. As the lab discussed, The circular fracture pattern could result from the deposition of a deposit over a buried impact crater. Perhaps the nose is a volcanic or mud vent and the deposit would be lava or mud flows?
This is a classic case of pareidoliathe psychological effect in which the brain sees shapes it recognizes in random patterns. The Martian bear adds itself to a long series of space illusions, ranging from the well-known “Man in the Moon” to the legendary “Face on Mars”. As Scientific American observes, “Our brains are wired to see faces, which isn’t too surprising, seeing as how they are the main way we recognize other people.”
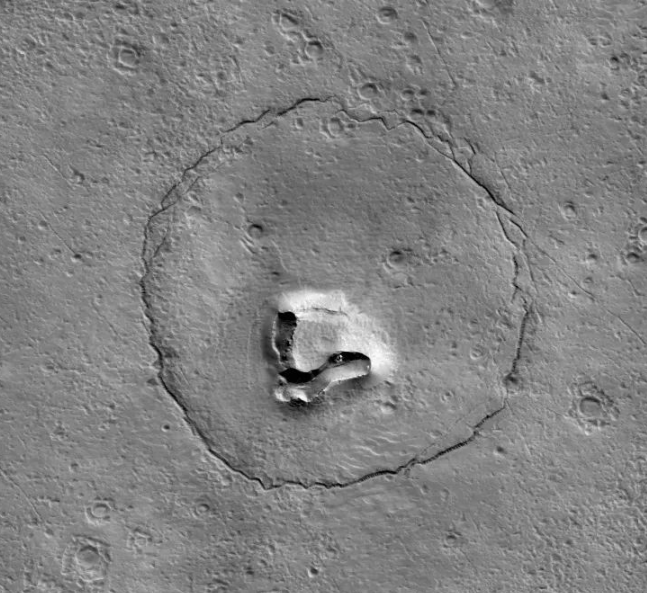
2. The Face on Mars: From Alien Monument to Optical Illusion More
Martian formations have inspired public fantasy than the infamous “Face on Mars.” Discovered in 1976 through photographs by NASA’s Viking 1 orbiter, the mesa within the Cydonia region seemed to possess two eyes, a nose, and a mouthtriggering decades of theorizing over lost civilizations. Subsequently, high-resolution photographs from the Mars Global Surveyor and Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter told the truth: the face is merely a natural mesa, its human appearance due to lighting and low image resolution.
The phenomenon highlights the way pareidolia influences our understanding of the universe. According to Scientific American, “True believers in the face on Mars had fallen prey to a psychological phenomenon called pareidolia, our brain’s tendency to impose a recognizable pattern on a visual stimulus.” Mars becomes a canvas for both geology and imagination.
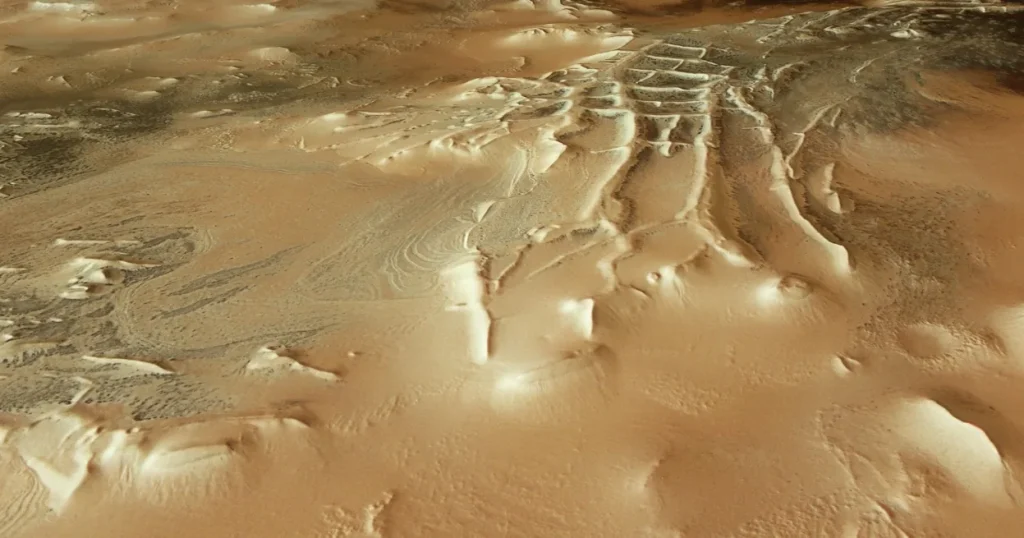

3. The Inca City and Other Martian ‘Ruins’
At Mars’ south pole lies a maze of rock formations, the “Inca City,” which has confounded scientists and invited outlandish speculation on lost Martians since scientists first described it. The European Space Agency (ESA) defines the formation as an array of high sand dunes that have been cemented into stone over millennia, which may be part of a vast impact crater 53 miles (86 km) across. Though the similarity to earthly ruins is startling, the reason lies in the geological history of Mars.
As stated by Marspedia, “Mars has an incredibly old history book of the past that is missing on Earth. Plate tectonics and intense air and water erosion has destroyed almost all the Earth’s past geology. Conversely, most of the surface of Mars is billions of years old.” These surface features, formed by wind, water, and volcanoes, produce structures which can look eerily man-made.
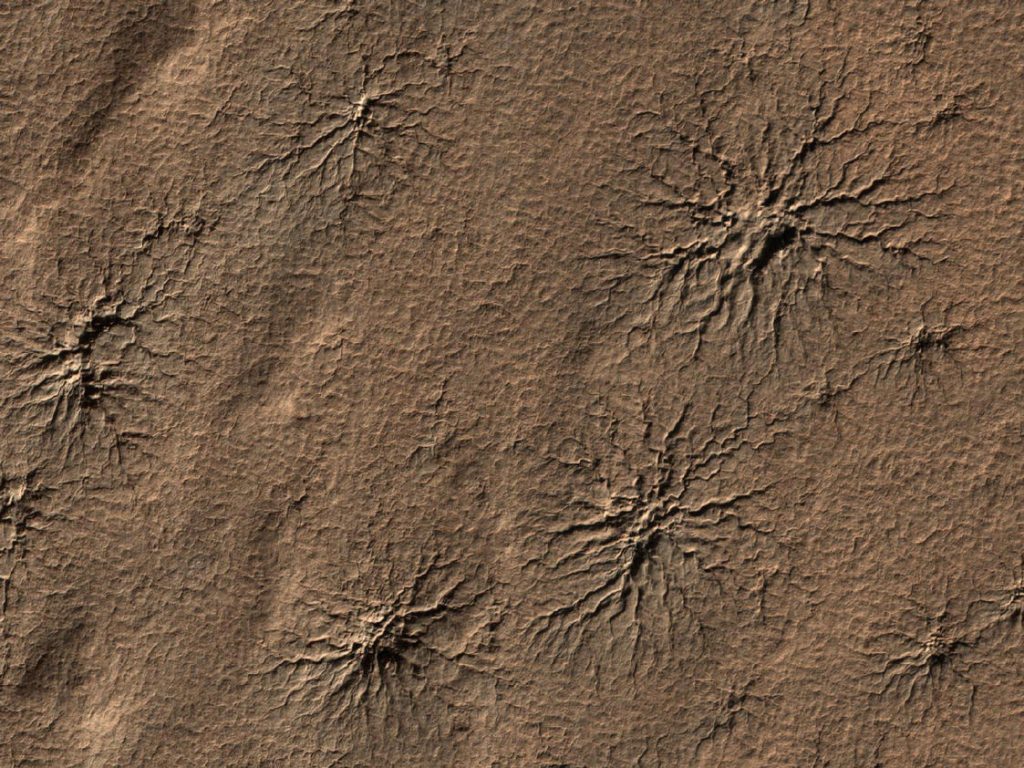

4. Martian ‘Spiders’: The Springtime Eruption of Araneiforms
Each southern spring, the Martian poles erupt in thousands of black, spider-like patternssome reaching widths of as much as a kilometer. These so-called “spiders” are not living organisms, but rather the byproduct of a distinctly Martian phenomenon: sunlight pours into transparent carbon dioxide ice, warming the ground beneath and making the ice sublimate. The resultant gas accumulates pressure until it bursts, spraying dark dust onto the planet’s surface in branching, spider-shaped forms. As Marspedia explains, In certain regions, numerous geyser-like eruptions of dark dust and gas are present.
High pressure dust and gas burst out of the ground. Winds tend to blow eruptions into dark plumes. After numerous observations, scientists determined that what occurs is a transparent-translucent slab of dry ice forms in the winter.” With more sun in the spring, stress accumulates under this slab as light warms cavities beneath the slab and converts dry ice to a gas.”
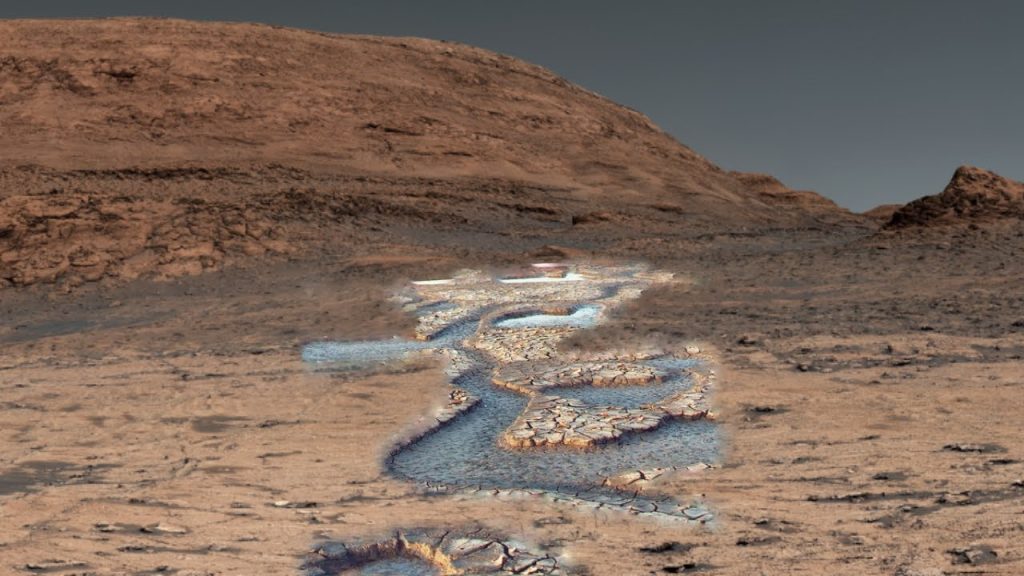

5. The Legacy of Water: Blueberries, Mud Cracks, and Ancient Lakes
Some of the most scientifically important Martian anomalies are those that suggest a more watery past. The discovery by the Opportunity rover of iron-rich “blueberries”small, round concretionswas early proof that the planet’s surface was once sculpted by liquid water. These smooth-surfaced spherules, polished by water hundreds of millions of years ago, are present in large numbers and continue to attract astrobiological study.
In other areas, Curiosity has discovered polygonal mud cracks that look like a “tile floor,” aged 3.8 to 3.6 billion years. Such structures, combined with layered sedimentary rocks and the remains of former lakes, back the hypothesis that Mars had environments with potential for life at one time. As Number Analytics points out, “The Curiosity Rover has provided extensive evidence of ancient lakes and rivers in Gale Crater, including sedimentary rocks that formed in a lacustrine environment.”
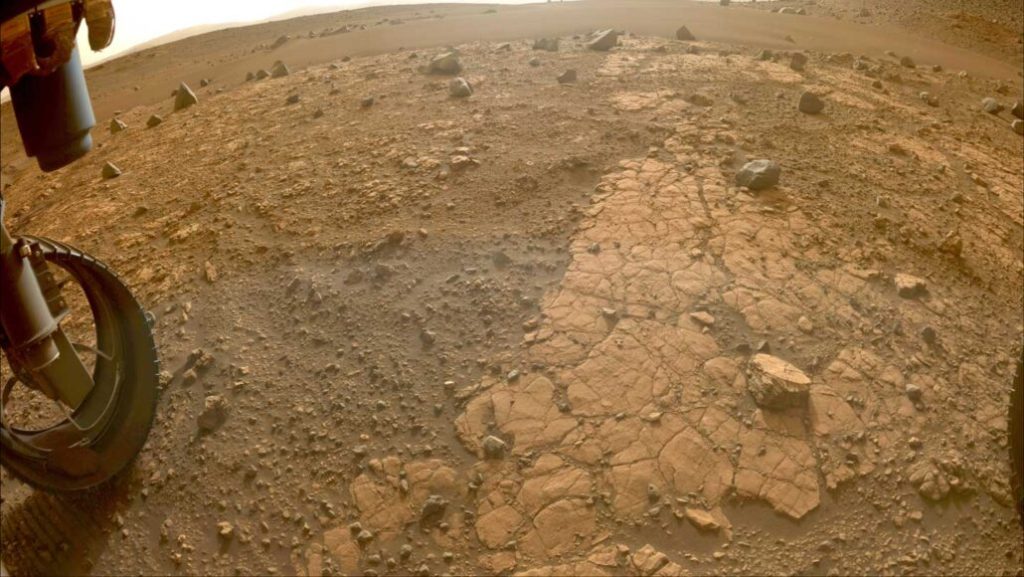

6. Martian Dust Devils and the Towering White Column
Dust devilstumbling columns of air and dustare ubiquitous on Mars, but some are positively enormous. In 2023, NASA’s Perseverance rover snapped a photo of a white dust devil towering above the ground, five times the height of the Empire State Building. NASA says that these vortices are created when updrafts of warm air collide with down columns of cold air, and that they can total as many as 145 million per day.
Dust devils are important to Mars’ active environment, dispersing dust and even dusting off the solar panels of landed vehicles. As Marspedia comments, “Another thing that creates light and dark patterns is a dust devil. These little tornadoes sweep away the bright dust and leave straight and/or curved trails. They are not uncommon particularly in regions with a lot of dust cover and at particular times of day.”
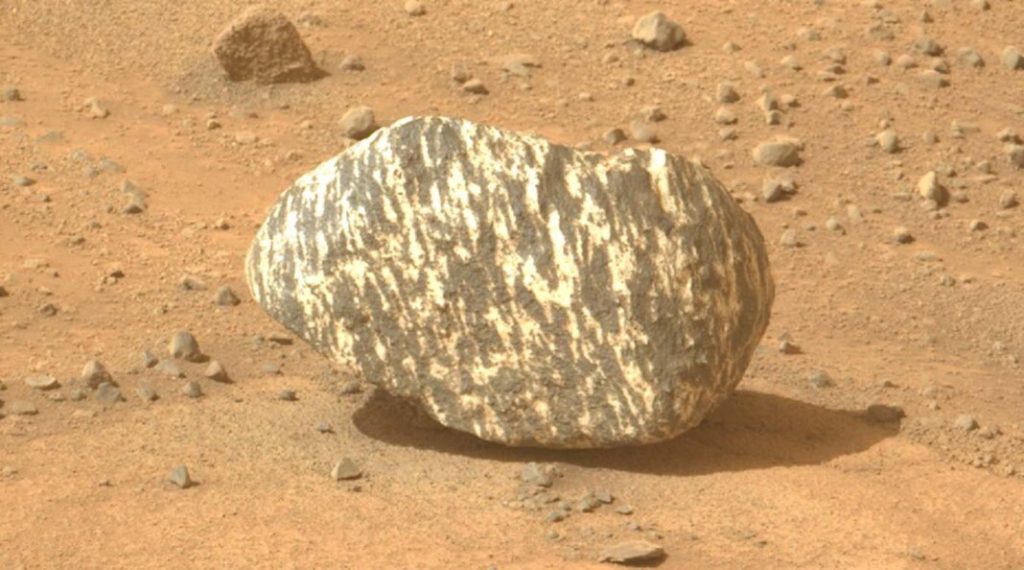

7. Meteorites and Out-of-Place Rocks: Afar Clues
Strewn about the Martian landscape are rocks that appear to have come from another world. The Curiosity rover found a rough, gray boulder known as Ames Knob, undoubtedly a meteorite that crash-landed on Mars millions of years ago. Such meteorites are not merely space junk; they are time capsules, providing clues to the planet’s past climate and atmosphere. And like that, Perseverance has spotted unusually white rocks and green, drill-marked stones visible against the planet’s rusty red dust. Some of them might have been carried by ancient rivers, while others are probably pieces of far-off impacts.
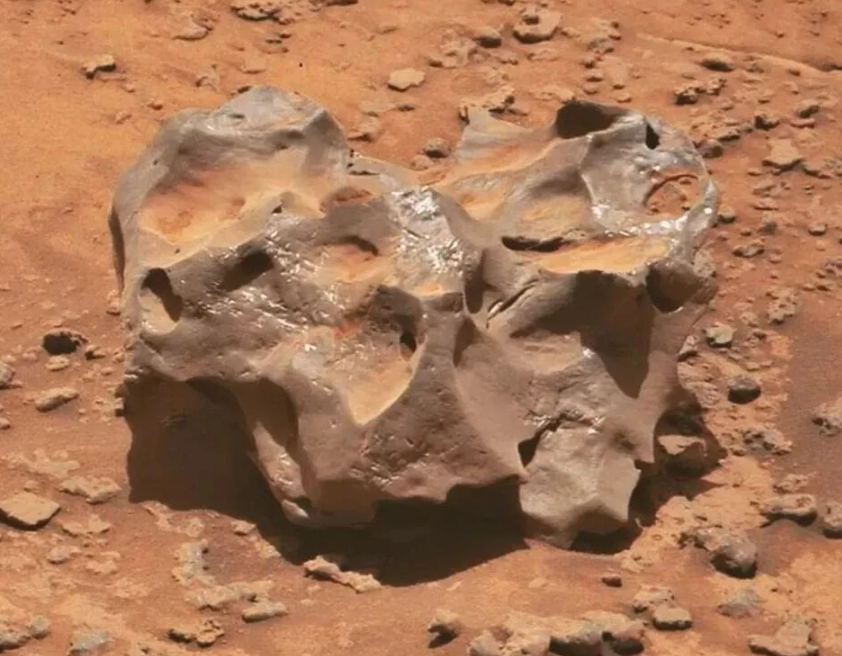

As NASA scientists elucidate, “Learning about the rock may be able to tell us about the past environment on the planet when the meteorite arrived, including whether it entered the land or in long-lost water.” Mars remains a planet of mysteries, its surface a patchwork of geological oddities and optical illusions. Each strange formation, whether born of ancient water, volcanic upheaval, or the quirks of human perception, deepens our understanding of both Mars and ourselves. As exploration continues, the Red Planet will undoubtedly yield more surprisesreminding us that in science, the line between the familiar and the unknown is often just a trick of the light.


